The College of Engineering is currently using the ‘Multisite’ feature that became available in WordPress version 3.0 this feature allows multiple virtual sites to share a single installation of WordPress. This is helpful in managing sites for security and with system updates, but does make access to administrative features different than the standard WordPress installation.
- Please contact engr-wpadmin@iastate.edu to request your College of Engineering affiliated WordPress hosting.
WordPress access/permissions
- Only a web browser is needed to access your WordPress site.
- Login in via yourdomain.iastate.edu/wp-admin with your ISUNetID (email prefix) and ISUNetID password.
Navigating WordPress

- (Dashboard) is the screen you will see after logging in and gives you access to the site management tools.
- Screen Options, found in the upper right corner, allows you to show/hide screen boxes. Boxes can also be rearranged by dragging and dropping.
- Help option, found in the upper right corner, gives you helpful descriptions about the screen you are on.
- Left-hand navigation menu provides the links to the various admin screens, with submenus showing on hover.
Posts
- Posts are linear/chronological. The default of WordPress is to display posts on the homepage in reverse chronological order (newest post first). In contrast to pages, posts usually have comments fields beneath them and are included in your site’s RSS feed. Posts can be organized within categories and tags.
- From WordPress: What’s the difference between categories and tags? Normally, tags are ad-hoc keywords that identify important information in your post (names, subjects, etc) that may or may not recur in other posts, while categories are pre-determined sections. If you think of your site like a book, the categories are like the Table of Contents and the tags are like the terms in the index.
- More info: http://codex.wordpress.org/Posts
Media
- The media library lists recent uploads first. Be sure to add descriptions for future referencing and alternate text (alt=”a description of your image”) for the visually impaired.
- Default file types: jpg, jpeg, png, gif, mp3, mov, avi, wmv, midi, mid, pdf, doc, and zip.
- The default file size limit is 2 MB.
- Please contact engr-wpadmin@iastate.edu if you would like to increase the size limit or add another file type.
Pages
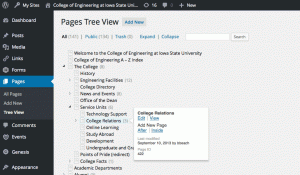
- Pages are typically used for content that is less time dependent.
- Pages can be setup with parent-child relationships, which can be useful in allowing WordPress to automatically generate a menu. They cannot be assigned to categories or tags.
- For sites with large numbers of pages, the college recommends activating the CMS Tree Page View plugin.
- More info: http://codex.wordpress.org/Pages
Comments
- Comments are typically used for post content. If you do allow them, set to be approved by Administrator.
Appearance
- Themes – Options include the default WordPress themes and a theme using the University color palettes. Other themes are allowed for student organizations and research groups, contact engr-wpadmin@iastate.edu for more information.
- Menus – Allows you to define your site’s navigation menu. Menus may contain links to pages, posts, categories or custom links. You can specify a different navigation label for a menu item as well as other attributes. You can create multiple menus. If your theme includes more than one menu, you can choose which custom menu to associate with each available menu area. You can also use custom menus in conjunction with the Custom Menus widget.
- Widgets – Independent sections of content that can be placed into specific spaces, called widgetized areas, provided by your theme. Widgetized areas are usually in the sidebars and can be shared across multiple pages/posts within a site. Location of widgetized areas vary from theme to theme. To populate your sidebars/widget areas with individual widgets, drag and drop the title bars into the desired area.
- Other Options – Depending on the theme you’re using, the Appearance tab may contain other options for controlling the ‘look and feel’ of the site
Plugins
- Plugins extend and expand the functionality of WordPress. You may activate or deactivate the plugins from the plugin screen. Engineering Tech Support maintains the list of allowed plugins. Feel free to make a request for a particular plugin for your site if what you are looking for is not available. Tech Support staff will test compatibility with the rest of the system and either add the plugin or assist in finding another solution if a conflict arises. Keep in mind that plugins are developed by third parties and support for a particular one may not keep pace with updates to the core WP files.
- Contact engr-wpadmin@iastate.edu to make a plugin request.
- The college does activates certain plugins with its default site setups.
Users
- This screen lists all the existing users for your site. Each user has one of five defined roles as set by the site admin: Site Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, or Subscriber. Users with roles other than Administrator will see fewer options in the dashboard navigation when they are logged in. Here’s a brief description of roles:
- Super Admin – Someone with access to the blog network administration features controlling the entire network (College Relations and Tech Support staff members)
- Administrator – Somebody who has access to all the administration features
- Editor – Somebody who can publish and manage posts and pages as well as manage other users’ posts, etc.
- Author – Somebody who can publish and manage their own posts
- Contributor – Somebody who can write and manage their posts but not publish them
- Subscriber – Somebody who can only manage their profile
When adding new users, be sure to fill out the required fields of username with ISUNetID (email prefix) and the email with the user’s ISU email address.
Tools
- Adminstrative tools for site management activities. Default tools are limited, but some plugins may add expand capabilities here.
Settings
- General Settings – Site name and administrative contact, an email confirmation required if the administrative contact is changed.
- Writing – Post writing options.
- Reading – Default of WordPress is to display a list of posts on the homepage. Most College sites are changed to display a static page.
- Discussion settings – Be sure to check the box for ‘An administrator must always approve a comment’.
- Media – Images sizes and embed settings.
- Privacy – Search engine visibility, typically you would want to allow search engines to catalog your site. During the development stage of your site, you might choose to turn that off.
- Permalinks – Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual pages and blog posts, as well as your category and tag archives. A permalink is the web address used to link to your content.
- Additional settings – May appear as plugins are activated.
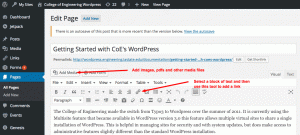
Adding content to Pages and Posts (Classic Editor*)
- Rich Text Editor – A WYSIWYG editor. Note: The backend display can differ from what appears on the frontend depending on style sheet settings of the site’s active theme.
- Add media (images, pdfs, etc.) with the Upload/Insert icon
- Don’t forget to add descriptive alternative text to when adding images to your pages. This text helps those visitors who might be assistive technology to access your content.
- Adding the Tiny MCE Advanced plug into your site will add more editing options to the Rich Text Editor, including table editing options.
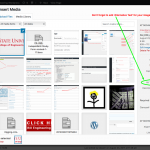
Add alternative text to your images
- Add media (images, pdfs, etc.) with the Upload/Insert icon
- Draft vs. Publish – Draft mode allows you to build pages and preview content without ‘publishing’ to the Internet.
- Visibility – Public, Password-protected, Private (accessible to only WordPress users)
- Page Attributes – Template options depending on your theme or create custom ones. Parent/Child relationships can be set through this box.
- Custom fields – Can be used for extra data depending on your theme or plugins.
* Starting with WordPress version 5.0, the Block Editor (also referred to as the Gutenberg Editor) became available. You can learn more about that editor here.